Regenerative medicine has evolved from the ancient concept of ‘regeneration’. In recent times, regenerative therapeutics are gaining scientific footing with a wide range of applications of stem cells.
Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) or adipose stem cells (ADSs) are isolated from adipose tissue and have multi-lineage potential, that is, possess the capability to differentiate into various cell types.
Historical Concepts and Regenerative Medicine Evolution
The idea of regeneration dates back to the studies of Aristotle and myths (Prometheus). In the early 20th century, the concepts of cell culture and organ transplantation evolved, followed by the stem cell revolution in the late 20th century. The concept of regenerative medicine substantially undertakes concepts including:
- Cell-based therapy
- Engineered scaffolds
- Scaffold implantation with cells
Hereby, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells serve as ideal candidates for regenerative medicine owing to their ability of self self-renewal.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
ADSCs are isolated from adipose tissue (fat) from distinct anatomical areas. These cells are abundant in the body. Researchers classify ASSCs as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that possess the ability to differentiate into several cell lineages. Some examples include adipogenic, chondrogenic and osteogenic cells under controlled laboratory conditions. The cells are characterized by the presence of specific biomarkers, including CD73, CD90 and CD105, and lack hematopoietic markers like CD34 and CD45. High availability, regenerative potential, and immunomodulatory properties of ADSCs make them ideal candidates in regenerative medicine research.
Adipose Tissue Stem Cells vs. Other Adult Stem Cells
Adipose tissue stem cells differ from other adult stem cells based on their source, abundance, and biological behavior. Some examples include:
- ADSCs vs. Bone Marrow–Derived Stem Cells: ADSCs are abundant and obtained with minimally invasive procedures. They demonstrate strong paracrine signalling abilities, thus facilitating strong cell-to-cell communication, the release of growth factors, and cytokines. This supports tissue repair and modulation of inflammation.
- ADSCs vs. Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): HSCs are limited to blood cell development, while ADSCs exhibit a broader range of differentiating potential.
Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (AD-MSCs)- Biological Characteristics
Biomarkers
AD-MSCs have adherent properties. The immunophenotype of AD-MSCs based on their antigen categories is as follows:
| Antigen Category | Surface-Positive Antigens | Surface-Negative Antigens |
| Adhesion | CD166 (ALCAM), CD105 (endoglin), CD54 (ICAM-1), CD49d (α4 integrin), CD29 (β1 integrin), CD9 (tetraspan) | CD104 (α4 integrin), CD62 (E-selectin), CD56 (NCAM), CD50 (ICAM-3), CD18 (β2 integrin), CD11b (αb integrin) |
| Receptor | CD44 (hyaluronate), CD71 (transferrin) | CD16 (Fc receptor) |
| Stem Cell | CD34, ABCG2 | — |
| ECM | CD90, CD146, Collagen types I & III, Osteopontin, Osteonectin | — |
| Cytoskeleton | α-smooth muscle actin, Vimentin | — |
The knowledge of the Immunophenotype of AD-MSCs enables researchers to isolate highly pure stem cells from heterogeneous populations.
Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
AD-MSCs possess strong immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. These cells regulate the activity of T cells, B cells, macrophages, and natural killer cells. They secrete various growth factors, proteins and cytokines that reduce inflammatory response and mitigate the immune rejection challenge. This promotes tissue healing.
Source and Isolation
Adipose Tissue Stem Cells harvesting methods involve:
- Primarily derived from human adipose (fat) tissue; common areas abdomen, thighs, or flanks
- Rich source of MSCs
- Harvested using a minimally disruptive protocol
- Undergoes isolation of stromal vascular fraction (SVF)
- Isolation involves washing, enzymatic digestion, and centrifugation to isolate ADSCs
- Characterization based on cell viability, morphology, and surface marker expression
ADSCs Mechanism of Action in Regenerative Therapies
- Tissue repair
- Cellular regeneration
- Paracrine signaling
- Secretion of growth factors

Clinical Applications
Clinicians believe in the potential application of ADSCs in various problems. The cells get differentiated into distinct lineages, including:
- Adipocytes
- Chondrocytes
- Glial Lineages
- Neuronal Lineages
- Beta-islet cells
- Osteoblast
- Muscle Cells
- Hepatocytes
- Keratinocytes
- Endothelial Cells
The primary clinical application includes:
Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal Disorders:
- Repair bone, cartilage regeneration and connective tissue
- Tendon reconstruction and Skeletal muscle repair
- Reduce inflammation and regenerate tissue in conditions like osteoarthritis, degenerative joints and tendon injuries
- Promotes extracellular matrix production and supports structural integrity
Neurological and Autoimmune Conditions
- Secretes bioactive molecules, supports neural tissue repair
- Reduces chronic inflammation, immune dysregulation and nerve damage
Wound Healing, Dermatology, and Aesthetic Medicine
- Promotes angiogenesis, skin regeneration, and collagen synthesis
- Paracrine activity supports faster tissue repair
- Tissue revitalization- scar management, skin rejuvenation and hair regrowth
Advantages
The following are the advantages of Adipose Stem Cells therapy:
- Higher stem cell yield compared to bone marrow
- Strong regenerative potential facilitates cell differentiation and paracrine signalling
- High proliferation
- Multipotent, the ability to differentiate into various lineages
- Promotes angiogenesis, anti-apoptotic and tissue remodeling
- Facilitates vascularization, improves oxygen supply
- The immunomodulatory effect suppresses excess inflammation, reduces the possibility of immune rejection
- Minimally invasive collection possesses ethical advantages.
Preclinical & Clinical Evidences
Preclinical and Clinical studies have widely explored the potential of ADSCs in regenerative studies. Some examples include:
- In-vitro and preclinical studies demonstrated osteogenic differentiation
- Clinical evidence showed use of ADSCs successfully repaired a post-traumatic calvarial defect in a seven-year-old child.
- Intra-articular (IA) injection with ADSCs repaired damaged cartilage in patients with osteoarthritis. Clinical symptoms showed significant improvement in the 6-month follow-up.
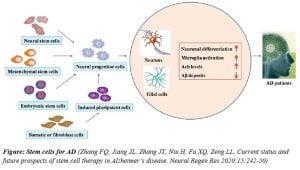
- NCT03117738: ADSCs for Alzheimer’s disease, study under investigation
- NCT02184546: ADSCs for Parkinson’s disease, under investigation
Limitations & Challenges
The following are the significant challenges associated with Adipose stem cell therapy:
- Standardization challenges in stem cell therapy
- Potential concern for tumorigenicity due to the presence of pro-angiogenic and immunoregulatory potential
- Lack of long-term clinical data
- Uncertain clinical efficacy translation
- Donor-dependent variability (age, metabolic condition, exposure to radiation)
- Variable complications and different regenerative capabilities of the adipose-derived stem cells
- Future directions in adipose-based regenerative medicine
Regulatory Status and Clinical Use Considerations
- Global regulatory overview
- Regulated in the name of cell-based or biological products
- Regulatory classification depends on the level of cell manipulation.
- ADSCs used must be of superior quality with no manipulation.
- Regulatory frameworks are evolving with new clinical evidence
What Causes Variability in Adipose Stem Cell Therapy Outcomes
- Patient’s age, medical history, metabolic health, and other health conditions
- Donor-related factors in the case of autologous stem cell use
- Harvesting and Isolation Procedure for stem cell isolation
- Ethical compliance and regulatory approval for stem cell use
- Researchers must use superior-quality stem cells to ensure effective study outcomes.
*NOTE: It is essential to use superior quality stem cells to ensure efficacy and reliability. Kosheeka, Noida, is among the leading suppliers of superior-quality stem cells for research purposes
Product-Related Queries, Or Partnership Inquiries
Conclusion
- ADSCs rich, reliable source of MSCs
- Multipotent differentiating capability
- Strong paracrine signaling facilitates tissue repair, immune modulation and angiogenesis.
- Preclinical and Clinical studies demonstrated regenerative outcomes.
- Advanced research using premium-quality stem cells must be conducted to develop a standardized protocol and draw conclusive results.
FAQ’s
Q- What are adipose-derived stem cells?
Adipose-derived stem cells or ADSCs are MSCs that are isolated from adipose or fat tissue. These cells possess regenerative potential through differentiation and paracrine signalling.
Q- How vital is Adipose stem cell therapy in regenerative medicine?
Adipose stem cells possess regenerative properties that can boost regenerative signalling, angiogenesis, anti-apoptotic properties, and facilitate revascularization.
Q- What factors influence the effectiveness of Adipose stem cell therapy?
Some factors, including donor age, source of adipose tissue, isolation procedure, and quality of cells, influence the biological behaviour and regenerative potential of stem cells.
Q- What are the safety concerns associated with adipose-derived stem cells’ clinical application?
Preclinical and early clinical studies showed encouraging safety profiles. Ongoing research must address long-term safety, risk factors, and standardization of therapy protocol.