Why Access to Fresh Biofluids is Critical to Your Research?
Fresh biofluids are known as the best option mimicking the living tissue in the human body. Especially for ongoing research in the field of oncology, the easy accessibility to freshly isolated biofluids can expedite the process of early-stage immunotherapies. Human biofluids refer to the bodily fluids circulating in our bodies, including blood, serum, plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluids, etc. These biofluids are packed with a range of biomarkers, signaling molecules, and circulating exosomes. Modern science is using them as reference material to get insights into health, disease profiles, and therapeutic interventions. With the exclusive set of information these biofluids carry, they are critically acclaimed as invaluable tools required at every stage of drug development; right from discovery studies, feasibility, and validation to the safety and efficacy assessments.
Drawbacks Of Using Dated Biofluids In Research
The frustration of working with dated blood samples or facing difficulties in locating the precise samples needed for a particular project is a common experience. These challenges not only impede the research process but also force researchers to work with suboptimal cell sources, consequently compromising the transferability, accuracy, and reliability of their collected data.
Some of the important reported challenges, while working with dated biofluids include:
Degradation of Biomolecules
The important biomolecules may degrade over the period, due to multiple freeze-thaw processes, and longer preservation time; which further compromises the integrity of these biofluids, leading to inaccurate outcomes in genomics, proteomics, and metabolic studies.
Loss of Cellular Viability and Functionality
Many biofluids like whole blood, plasma, seminal fluids, cerebrospinal fluids, etc. carry live contain live cells, along with important biomolecules. With dated samples, researchers often face difficulties of batch-to-batch variation in understanding cellular response, immune functionalities, and signaling pathways due to loss of cellular viability and functionality. 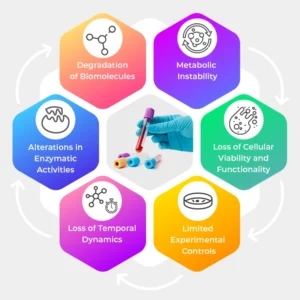
Alterations in Enzymatic Activities
In the case of studies related to the determination of enzyme kinetics, substrate turnover, and/or determination of enzyme inducers, frozen samples may fail to accurately represent the in vivo enzymatic environment.
Metabolic Instability
Studies related to various metabolic processes are highly dependent upon the metabolic stability of the biofluids. With longer storage, it is impossible to achieve the desired stability in the given biofluids. Apart from longer storage, various factors can affect the metabolic stability of the biofluids, including changes in the concentration, repeated freeze-thaw, alterations in the storage conditions, etc.; further affecting the reliability of metabolic profiling and metabolic research.
Loss of Temporal Dynamics
A thorough understanding of certain dynamic biological processes can be accurately achieved in fresh biofluids that have accurately captured temporal variations in the composition, which is generally influenced by circadian rhythms, meal intake, and/or diseased progression.
Limited Experimental Controls
Comparing controls obtained from fresh biofluids with those of dated ones is a tedious task, due to the unavailability of reliable experimental controls stored with similar physiological conditions.
Thus, considering the criticality of their usage in various experimental processes, addressing the hurdles in accessing quality blood products becomes imperative to ensure the progress and success of research endeavors in these diverse and vital fields.
How To Maintain The Integrity Of Biofluids
Utilizing fresh biospecimens in research offers numerous advantages, particularly in functional assays where complications from cell activation or modification due to the freeze/thaw process can be avoided. Fresh cells and biospecimens provide stable components, facilitating studies on cell activation states, cell surface markers, and various intracellular and extracellular molecules.
Here are some prominent applications for fresh biospecimens:
- Fractionation: Performing processes like fractionation on whole blood is more feasible and effective when conducted soon after blood is drawn. Freezing blood before fractionation can result in elevated levels of circulating DNA and toxins due to cell lysis and granulocyte activity.
- Point of Care Device Testing Services: Fresh blood, urine, saliva, and other specimens are valuable for testing Point of Care devices, ensuring accurate results in scenarios reflecting real-world usage. This service aids in validating PoC devices by emulating the conditions under which they will be employed.
- Flow Cytometry Assays: Fresh blood is advantageous in flow cytometry (FC) assays as the cells are more viable, allowing for the capture of a greater number of cellular events. Certain cells, like dendritic cells, do not freeze well, and their presence may be compromised in FC analyses without the use of fresh blood.
- Functional Cell-Based Assays: Fresh blood is essential for functional assays, ensuring the activity and stability of blood components like cells and molecules. It enables the analysis of microsomes and inflammasomes and is crucial for assessing the presence of various functional elements.
Challenges in Isolating Cell Subsets: Isolating cells and cell subsets for functional cell-based assays pose challenges, including low cell yields and suboptimal downstream results. The isolation process, cell lysis, and centrifugation effects contribute to these challenges, emphasizing the importance of fresh blood.
- Importance of Fresh Blood for Antibody Studies: In studies involving antibody functionality and B cells, fresh materials are optimal. Thawing often results in the rupture of B cells, hindering the study of antibody genetic rearrangement. Fresh blood is crucial for preserving B cells and dendritic cells, which may not survive the freeze/thaw process.
- Neutrophil Functional Assays: Neutrophil functional assays, including studies on migration, require fresh biospecimens. Neutrophils, with a limited lifespan, are prone to activation, and the freeze/thaw process may compromise their functionality. Fresh blood is essential for accurate studies on cytokine secretion and NK cytotoxicity activity related to neutrophils.
Product-Related Queries, Or Partnership Inquiries
Pivotal Role of Fresh Blood Products in Advancing Clinical Breakthroughs
 Fresh blood products have played a crucial role in spearheading cutting-edge research programs, contributing to significant advancements in recent years. Two notable clinical breakthroughs, liquid biopsies, and CAR-T therapy, stand out as exemplary instances where the utilization of fresh blood products from healthy patients has been instrumental in pioneering transformative medical developments.
Fresh blood products have played a crucial role in spearheading cutting-edge research programs, contributing to significant advancements in recent years. Two notable clinical breakthroughs, liquid biopsies, and CAR-T therapy, stand out as exemplary instances where the utilization of fresh blood products from healthy patients has been instrumental in pioneering transformative medical developments.
Liquid Biopsies: A Non-Invasive Milestone in Cancer Detection
One noteworthy clinical advance is the emergence of liquid biopsies, exemplified by the FDA’s 2016 approval of the cobas® EGFR mutation liquid biopsy test for detecting lung cancer. This approval marked a substantial leap forward, offering a safe, non-invasive, and easily repeatable alternative to traditional tissue biopsies. The use of fresh blood products was integral to the development of these tests, enabling companies to explore and expand their applications. This innovation not only enhances patient experience but also provides researchers with a powerful tool for obtaining critical biological insights.
CAR-T Therapy: Revolutionizing Cancer Treatment
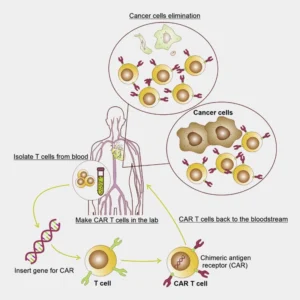 The second groundbreaking development is CAR-T therapy, a potential revolution in cancer treatment. This therapy involves modifying T-cells to produce chimeric antigen receptors on their surface, effectively targeting and eliminating cancer cells. The initial development of CAR-T therapy hinged on the use of fresh blood products from healthy donors. This approach has since paved the way for a paradigm shift in cancer treatment strategies, demonstrating the transformative potential of utilizing fresh blood products in therapeutic breakthroughs.
The second groundbreaking development is CAR-T therapy, a potential revolution in cancer treatment. This therapy involves modifying T-cells to produce chimeric antigen receptors on their surface, effectively targeting and eliminating cancer cells. The initial development of CAR-T therapy hinged on the use of fresh blood products from healthy donors. This approach has since paved the way for a paradigm shift in cancer treatment strategies, demonstrating the transformative potential of utilizing fresh blood products in therapeutic breakthroughs.
Essential Role of Fresh Blood Products in Generating Relevant Results
The reliance on fresh blood products proved to be indispensable for generating results that offer genuine biological insights and drive significant advances in clinical applications. The unique characteristics of fresh blood samples, such as their immediate molecular and cellular composition, have been fundamental in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and relevance of research outcomes. As more companies embark on developing similar innovative tests and therapies, the need for a steady supply of fresh blood products remains paramount to sustaining progress and innovation in the realm of medical research and treatment.
Biofluids In Drug Discovery And Development
 Exciting advancements have been made in the field of electrochemical sensing methods for various biofluids, particularly in drug discovery and development with significant clinical relevance. Many studies have utilized materials such as multi-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene for electrode modification due to their reported fouling resistance to specific target species. Electrodes can efficiently sense and monitor pharmaceuticals in biofluids.
Exciting advancements have been made in the field of electrochemical sensing methods for various biofluids, particularly in drug discovery and development with significant clinical relevance. Many studies have utilized materials such as multi-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene for electrode modification due to their reported fouling resistance to specific target species. Electrodes can efficiently sense and monitor pharmaceuticals in biofluids.
Toxicology studies in drug development have an important role in investigating the safety and the risks associated with new pharmaceutical products. In these studies, various biofluids are utilized to understand how the drug metabolizes and responds in the body. Immunotoxicology focuses on investigating the adverse impact of drugs on the immune system. In drug discovery and development, toxicology and immunotoxicology studies are conducted simultaneously. In various stages of pre-clinical and clinical trials, biofluids are isolated at different times after drug administration to know the potential, toxic effects, drug pharmacokinetics, and metabolism. So, it is essential to utilize the fresh biofluids in research.
Conclusion
According to the Best Practices Guide by the International Society for Biological and Environmental Repositories (ISBER), it is recommended that blood samples undergo processing and storage within a timeframe of 1 to 24 hours post-draw, depending on the specific analytical endpoint. Beyond this window, the functionality of cells begins to decline, potentially leading to significant implications based on the intended application.
Recognizing the potential effects of utilizing suboptimal blood products, it is not surprising that many scientists are actively exploring the impact of processing times post-venepuncture on cell function. Several published studies now advocate for the immediate processing of blood products, emphasizing that ideally, this should be conducted as soon as possible after blood collection, with a recommended maximum delay of eight hours for storage at room temperature. These findings underscore the critical importance of timely and meticulous handling of blood samples to preserve cell functionality and ensure the reliability of research outcomes.
In summary, the use of fresh biofluids proves indispensable in various research applications, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of results in functional assays, downstream analyses, drug discovery and development, and toxicological studies.