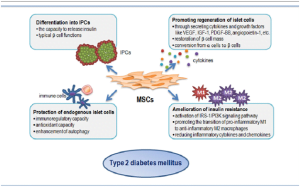
Cell-based therapy and especially stem cell therapy have gained a status as promising therapeutic field, to cure incurable diseases. Recently, China, USA, and Israel have conducted few stem cell-based human studies for COVID19 patients. Among all stem cells, Placental MSCs were used as a potential source of stem cells due to their high proliferation rate, low invasive procedure, and free of ethical issues and most importantly due to their immunomodulation properties. Following the novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection, immune overreaction triggers several destructions in the body was observed. The immune over reaction in COVID-19 patients is associated with production of large amounts of inflammatory factors, causing a cytokine storm including an overproduction of immune cells like effector T cells and natural killer cells. Endogenous repair by reparative properties of the stem cells also plays important role during antiinflammation reaction.
Although, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) does not have direct effect of viruses but studies revealed that MSCs do resist viral attack by the expression of interferon gamma stimulated genes (ISGs) which are expressed in MSCs prior to their differentiation. Hence, stem cells would be expected to survive even if transplanted into patient with active coronavirus infection. Also, rejuvenation and regeneration property of stem cells helps body in various processes involving reduction in inflammation, secretion of cell protective substances, transfer of mitochondria, reduction of cell death, anti-oxidative effects, and improvement of overall immune function. Also, there are direct evidence of stem cell protection against influenza virus (A/H5N1) infection, where MSCs helps in reversal of lung injury.
The limited available data from studies conducted so far unanimously revealed the intravenous injection of placental mesenchymal stem-cells into a covid-19 patient remarkably showed boost in the body’s immune response against the infection. The intravenous injection allows MSCs in circulation to home into lungs and help build up regenerative cells in the lungs, which could protect the epithelial cells of the lungs, prevent lung damage, and help patients recover.
With no available vaccine or a therapeutic approach, COVID-19 presents a serious and urgent healthcare crisis. The critically ill patients, who are not responding to the conventional pneumonia therapies and unlikely to recover needs something revolutionary like stem cell therapy. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has already approved clinical trials to study covid-19 patients who have been administered MSC derived from the placenta to prevent inflammation of lungs. Here, it is the beginning of the MSC therapy idea in the treatment of COVID-19 patients. Therapeutic approach is in its preliminary stages, and more pre-clinical data is required, particularly in models of coronavirus-induced lung injuries. While compassionate use of MSC-based therapies may be contemplated in different circumstances, we urge that whenever possible, this take place in the larger context of a clinical investigation.